-
Common NameParathion
-
中文通用名对硫磷
-
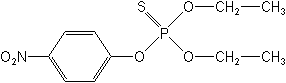
IUPACO,O-diethyl O-4-nitrophenyl phosphorothioate
-
CASO,O-diethyl O-(4-nitrophenyl) phosphorothioate
-
CAS No.56-38-2
-
Molecular FormulaC10H14NO5PS
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityInsecticide, acaricide
-
PremixParathion-methyl+trichlorfon
Parathion-methyl+phoxim
Parathion+trichlorfon
Methamidophos+parathion-methyl
Endosulfan+parathion-methyl
Cyhalothrin+parathion-methyl+isocarbophos
Dusts, emulsion concentrates, granules, ULV liquid, wettable powders.
Premix Parters: primisulfuron-methyl;
-
Physical PropertiesPale yellow liquid. Melting point 6.1°C. Hydrolyzes slowly at pH 7 or below. Specific gravity 1.26. Incompatible with alkaline materials. Readily soluble in dichloromethane, 2-propanol, toluene. Soluble in n-hexane.Molecular weight:291.3; Physical form:Pale yellow liquid, with a phenol-like odour. Density:1.2694; Composition:Tech. grade is 96-98%. Melting point:6.1 °C; Flash point:174 °C ( tech.); Vapour pressure:0.89 mPa (20 °C); Henry constant:0.0302 Pa m3 mol-1; Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 3.83; Solubility:In water 11 mg/l (20 °C). Completely miscible with most organic solvents, e.g. dichloromethane >200, isopropanol, toluene, hexane 50-100 (all in g/l, 20 °C).; Stability:Hydrolysed very slowly in acidic media ( pH 1-6), more rapidly in alkaline media; DT50 (22 °C) 272 d ( pH 4), 260 d ( pH 7), 130 d ( pH 9). Isomerises on heating ab.
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for rats c. 2, mice c. 12, guinea pigs c. 10 mg/ kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rats 71, female rats 76 mg/kg. Not irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for male and female rats 0.03 mg/l (aerosol). Phytotoxicity:Non-phytotoxic, except to some ornamentals, cucurbits, sorghum, and some varieties of apple, pear, and tomato.
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Algae: ErC50 for Scenedesmus subspicatus 0.5 mg/l.Bees:Toxic to bees.Daphnia: LC50 (48 h) 0.0025 mg/l.Fish: LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.5, golden orfe 0.58 mg/l.Worms: LC50 for Eisenia foetida 267 mg/ kg dry soil.
Environmental fate:
Animals:In rats, following oral administration, 4-nitrophenol and paraoxon were the principal metabolites excreted (M. P. Carver, Pestic. Biochem. Physiol., 1990, 38, 254; L. G. Sultatos & C. L. Gagliardi, Biochem. Pharmacol., 1Soil:Based on Koc values and leaching studies, parathion can be classified as a compound with low mobility. In biologically-active soils, parathion is rapidly degraded under laboratory conditions as well as in the field. The degradaPlant:The major metabolites are paraoxon, diethylphosphate, 4-nitrophenol and photometabolites S-ethyl parathion and S-phenyl parathion. WATER SOLUBILITY: 12.4 mg/l at 25°C -
Transport InformationSignal Word:DANGER; Hazard Class:Ib(Highly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Glyphosate price plummets 40% in one year in Argentina
Indian govt stops imports of herbicide Glufosinate priced below Rs 1,289 per kg
Carbendazim fungicide wins victory in Brazilian Parliament
Corteva presents new pre-emergent herbicide Linear for sugarcane in Brazil
Picloram Triclopyr Aminopyralid
Revolutionizing disease prevention: BASF launches new rice fungicide Cevya® in China
Thiamethoxam is allowed again in Brazil by a judicial decision
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide
Colombia’s Constitutional Court bans chlorpyrifos
ADAMA Canada moves forward with lambda-cyhalothrin sales for 2023

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe