-
Common NamePhosphamidon
-
中文通用名磷胺
-
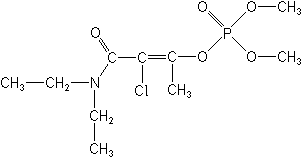
IUPAC(EZ)-2-chloro-2-diethylcarbamoyl-1-methylvinyl dimethyl phosphate
or
(EZ)-2-chloro-3-dimethoxyphosphinoyloxy-N,N-diethylbut-2-enamide -
CAS2-chloro-3-(diethylamino)-1-methyl-3-oxo-1-propenyl dimethyl phosphate
-
CAS No.13171-21-6
-
Molecular FormulaC10H19ClNO5P
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityInsecticide
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:299.7; Physical form:Pale yellow liquid. Density:1.21 (25 °C); Composition:The commercial compound contains 70% m/m (Z)- isomer (b- isomer) (which has the greater insecticidal activity) and 30% (E)- isomer (a- isomer). Vapour pressure:2.2 mPa (25 °C); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 0.79; Solubility:Miscible with water, acetone, dichloromethane, toluene and other common organic solvents, with the exception of aliphatic hydrocarbons, e.g. solubility in hexane 32 g/l (25 °C).; Stability:Rapidly hydrolysed by alkalis: DT50 ( calc.) (20 °C) 60 d ( pH 5), 54 d ( pH 7), 12 d ( pH 9).
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for rats 17.9-30 mg/ kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats 374-530, rabbits 267 mg/kg. Slight skin irritation; moderate eye irritation (rabbits). Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats c. 0.18, mice 0.033 mg/l air. Phytotoxicity:Non-phytotoxic, except to some varieties of cherry, plum, peach, maple and sorghum. ADI:( JMPR) 0.01 mg/ kg b.w. [1998].
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Bees:Highly toxic to bees.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail 3.6-7.5, mallard ducks 3.8 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for Japanese quail 90-250 ppm.Daphnia: LC50 (48 h) 0.01-0.22 mg/l.Fish: LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 7.8, fathead minnow 100 mg/l.Other aquatic spp.:Highly toxic to crustaceans.
Environmental fate:
Animals:In mammals, following oral administration, 85-90% of the dose is excreted within 24 hours, almost entirely in the urine. Complete metabolism occurs during the passage, by oxidative dealkylation of the amide group and hydrolysis of the phosphorus-ester bonPlant:In plants, an ethyl group is split off from the amide group, and, simultaneously or subsequently, the ester bond between the side-chain and the phosphorus atom is hydrolytically cleaved. WATER SOLUBILITY: Miscible -
Transport InformationSignal Word:DANGER; Hazard Class:Ia(Extremely hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Orthosulfamuron boosts sugarcane production, study finds
Glyphosate price plummets 40% in one year in Argentina
Indian govt stops imports of herbicide Glufosinate priced below Rs 1,289 per kg
Carbendazim fungicide wins victory in Brazilian Parliament
Corteva presents new pre-emergent herbicide Linear for sugarcane in Brazil
Picloram Triclopyr Aminopyralid
Revolutionizing disease prevention: BASF launches new rice fungicide Cevya® in China
Thiamethoxam is allowed again in Brazil by a judicial decision
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide
Related CompaniesMore
Sudarshan Chemical Industries Ltd.
Country: India

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe