-
Common NameDimethenamid-P
-
中文通用名精二甲吩草胺
-
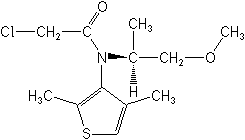
IUPAC(S)-2-chloro-N-(2,4-dimethyl-3-thienyl)-N-(2-methoxy-1-methylethyl)acetamide
-
CAS2-chloro-N-(2,4-dimethyl-3-thienyl)-N-[(1S)-2-methoxy-1-methylethyl]acetamide
-
CAS No.163515-14-8
-
Molecular FormulaC12H18ClNO2S
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityHerbicide.
Dimethenamid-P can be applied pre-plant (at the surface), preplant incorporated, pre-emergence and post-emergence (in corn to 36" tall). The best results are obtained when the product is applied to damp soil or when the application is followed by irrigation or a rain shower. The product provides season-long residual control and is effective in wet or dry conditions, providing a consistent level of grass control from year to year.
Isard will be recommended as part of the maize herbicide programme in France where it is reported to synergise the activity of certain broadleaf weed herbicides such as pendimethalin for pre-emergence treatment, or in sequence with bentazone for pre- then post-emergence treatment. Use of such a combination with pendimethalin or isoxaflutole (W0051), for example, is expected to reduce the need for post-emergence treatments by decreasing the number of new grass germinations and lowering the pressure of broadleaf weeds.
The product can also provide useful suppression of a number of important broadleaf weeds including goosefoot (Chenopodium album), Ambrosia artemisifolia,black nightshade (Solanum nigrum), purslane (Portulaca oleracea) and Polygonumspp plus the grasses Eriochloa villosaand Panicum milliacea.
The tolerance of chicory to pre-emergence application of dimethenamid-P was established in a weed free experiment (www.ridgetownc.on.ca/weeds/Reports/ 2000/2000Chicory.pdf). Use of this product at 750 and 1500 g ai/ha was found to cause high visual crop injury and a reduction in yield.
In 2003, the Washington State Commission funded two projects using dimethenamid-P for the control of weeds. In the first project, dimethenamid-P had been shown to exhibit some selectivity in cucumbers at reduced rates in preliminary tests carried out at the Washington State University (WSU). Consequently, Dr Tim Miller plans to evaluate dimethenamid-P applied alone and in combination with halosulfuron, clomazone, ethalfluralin and bentazon both pre- and post-emergence for efficacy, crop safety and weed control in various cucurbits in the 2003 growing season; completion of the trial is expected in November. In the second project, dimethenamid-P will be evaluated on hops for the control of redroot pigweed (Amaranthus retroflexus) by Dr Doug Walsh from the Irrigated Agriculture Research and Extension Center at WSU; there is currently no effective chemical alternative. The trials will support registration in Washington, with full registration expected by 2008.
Research evaluating the use of dimethenamid-P for weed control in potatoes was carried out at Oregon State University in 2000. There was significant stunting at the higher rates (0.24 and 0.47 kg/ha) in mid-May but no significant injury was apparent in mid-June and the yield of potatoes was not reduced, even at the high rates. In 2001, field trials were conducted on potatoes in Idaho, Oregon and Washington, applying dimethenamid-P at 0.12 kg/ha alone or in combination with EPTC (0.55 kg/ha), metribuzin (0.09 kg/ha), pendimethalin (0.18 kg/ha), rimsulfuron (0.004 kg/ha) or pendimethalin plus metribuzin. The herbicides were applied after hilling, prior to potato and weed emergence, and sprinkler incorporated immediately after application. Season-long control of redroot pigweed was improved by tank mixing dimethenamid-P with pendimethalin or EPTC compared to pendimethalin or EPTC alone. Similarly, control of common lambsquarters was improved by the addition of dimethenamid-P to EPTC, pendimethalin or rimsulfuron compared to use on their own, whilst tank mixing with EPTC, metribuzin, pendimethalin or rimsulfuron improved hairy nightshade control. A request by the Idaho Department of Agriculture to the US EPA to use dimethenamid-P on potatoes for the control of hairy nightshade was denied in 2002 as an adequate alternative was available. -
CropUsedry beans, grass seeds, maize, peanuts, sorghum, soybeans, sunflowers, sweetcorn
700-1000 g ai/ha
1008 g ai/ha (France, maize, as atrazine replacement)
-
Premixchlorothalonil; copper oxychloride; folpet; mancozeb; prochloraz triphenyltin hydroxide.
-
Physical PropertiesDark brown liquid with aromatic odor. Melting point at 760 mmHg. Specific gravity 1.127 g/ml. Vapor pressure 1.88 x 10-5 at 25°C (mmHg at 20°C).
-
Toxicology(Rat): Oral LD50 695 mg/kg (male, female); Inhalation LC50 (4 h) >5.6 mg/l; Dermal LD50 >2000 mg/kg.
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Fish: LC50 (96 h) 6.3 mg/l (rainbow trout); 10 mg/l (bluegill sunfish); EC50 (48 h) 12 mg/l (Daphnia). Bird: Oral LD50 1068 mg/kg (bobwhite quail); Dietary: LC50 (8 d) >5620 ppm (bobwhite quail, mallard)
WATER SOLUBILITY: Emulsifiable.
Daphnia magna[48 h]
ED50 12 mg/L
Bee [oral, 48 h]
LD50 = 205 μg/bee
Rainbow trout [96 h]
LC50 = 6.3 mg/L
Bee [contact, 48 h]
LD50 = 1373 μg/bee
Lemna gibba[7 h]
EC50 0.016 mg/L
Green alga [72 h]
EC50 0.017 mg/L
Earthworm [14 d]
LC50 = 294.4 mg/kg soil
Fate in soil:
Dimethenamid is rapidly degraded in the soil with a half-life of 7-13 days. The Koc value is 155 ml/g. Lysimeter and modelling studies suggest that there is no risk of groundwater contamination. -
Transport InformationSignal Word:WARNING; Hazard Class:II (Moderately hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
France approved BASF’s Tanaris®/Solanis® herbicide on winter oilseed rape
BASF introduces Armezon Pro to control glyphosate resistant weeds in Canada

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe