-
Common NameEtoxazole
-
中文通用名乙螨唑
-
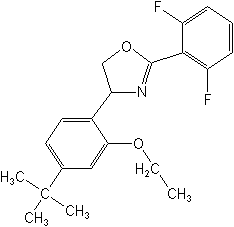
IUPAC(RS)-5-tert-butyl-2-[2-(2,6-difluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-4-yl]phenetole
-
CAS2-(2,6-difluorophenyl)-4-[4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-2-ethoxyphenyl]-4,5-dihydrooxazole
-
CAS No.153233-91-1
-
Molecular FormulaC21H23F2NO2
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityInsect Growth Regulator/Acaricide
Etoxazole is an IGR with contact activity against eggs, larvae and nymphs of mites. It has very little activity against adults but can exert ovicidal activity in adult mites. The eggs and the larvae are particularly sensitive to the product, which acts by inhibiting respiratory organ formation in the eggs and moulting in the larvae. In Japan, laboratory tests have shown that this activity is not affected by temperature changes in the range 15-30°C. In field trials, etoxazole has shown residual activity against mites lasting up to 35 days on fruit.
Yashima reports that the compound has translaminar activity, able to control target pests not directly exposed to the application spray, e.g. on the lower surfaces of leaves; this is a major advantage for growers in situations where underleaf spray coverage is difficult to achieve. Etoxazole has shown no phytotoxicity on the crops tested and has been shown to be safe to beneficial species.
Philagro recommends application of Bornéo to fruit trees at the end of egg hatching in spring. In vines, the treatment should be made from the beginning of pest colonisation on the young growths up to stage G (where the grapes have separated). The product is most effective while the mite populations are low; in cases where numbers are high, a tank mix with an adulticide is recommended. A second application of etoxazole can be made 14 days after the first. On pome fruit and strawberries, Zeal can be applied at early season (tight cluster to petal fall) or in full season when mite populations reach economic thresholds.
Etoxazole is active against aphids and mites resistant to commercially available insecticides/acaricides. In field trials it gave equal or better control than commercial standards at low application rates. In greenhouse applications, Tetrasan is approved in the US for the foliar control of citrus red mites, European red mites, Pacific spider mites, southern red mites, spruce spider mites and twospotted spider mites on bedding plants, foliage plants, fruit trees, ground covers, nut trees, and woody shrubs. Zeal does not control rust mites or blister mites on pome fruit and grapes or cyclamine mite on strawberries. It is not recommended for use on poinsettia after bract formation.
Miticide field trials in Florida (Berry & Veg. Times, 2002) showed good results from etoxazole (Zeal) applied alone or in combination with Danitol. In pest management tests on apple trees (Malus domestica) at West Virginia University (AMT 28), a summer application of etoxazole (Zeal) resulted in slower knockdown of European red mite than Pyramite but the etoxazole treatment was superior in providing the lowest level of accumulated mite-days.
A field trial conducted in an eight-year old orchard at the Jordan Station in Ontario, Canada to assess various acaricides for the control of European red mite on apple showed that, in a 7-day sample, only the plots treated with etoxazole contained significantly fewer European red mite motiles than the control. In the 21-day sample, etoxazole and Pyramite treatments contained fewer European red mite motiles than Floramite and significantly less than the untreated control. Numbers of beneficial mites in treated plots were equivalent to the control in the 7-day and 14-day samples, while numbers in the plots treated with etoxazole were significantly lower than in control plots in the 21-day sample. Whether these differences were due to toxic effects or a lack of prey was not determined.
At Washington State University, investigations were carried out in 2003 to address the sublethal effects of novel insecticide chemistries on beneficial insects, specifically, undesirable effects on the reproductive potential of predators and parasitoids. Studies conducted to assess the effect of pesticides on fecundity and survival of predatory mites (Typhlodromus occidentalis) after exposure to various insecticides in laboratory bioassays (Orchard IPM Update, 2003) showed that etoxazole (Secure) had no effect on fecundity or residency of T occidentalis at a high field rate. Conversely, the two chloronicotinyls tested [thiamethoxam (Actara,P0053) and imidacloprid (Provado)] both showed effects on T occidentalis.
Against beneficial species: Valent reports that Zeal may exert a moderate effect on the thrips predator, Orius spp, certain predatory mites (Typhlodromus spp) and the green lacewing (Chrysoperla carnea); little or no effect on pear psylla predator (Anthocoris melanocerus), the plant bug, Pilophorus spp and the aphid predator, Harmonia axyridis, and no effect on the whitefly parasite, Encarsia formosa, the predatory beetle, Aleochara bilineata, the parasitic wasp, Aphidius rhopalosiphi, the predatory thrips, Scolothrips takahasii or the predatory mite, Neoseiulus californicus.
Studies on the genetic basis of resistance to two acaricides, chlorfenapyr and etoxazole, which have different chemical structures and modes of action, have been conducted in the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae (J. Econ. Entomol, 2002). The resistance ratios calculated from the LC50 of resistant and susceptible strains were 483 for chlorfenapyr and >100.000 for etoxazole. Mortality caused by the two acaricides in F1 progeny from reciprocal crosses between the resistant and susceptible strains indicated that the modes of inheritance of resistance to chlorfenapyr and etoxazole were completely dominant and completely recessive respectively. Mortality in the F2 progeny indicated that for both acaricides, the resistance was under monogenic control. Repeated backcross experiments indicated a linkage relationship among the two acaricide resistances and malate dehydrogenase, although phosphoglucoisomerase was not linked with them. The recombination ratio between the resistances was 14.8%. Results suggest that heavy spraying of the two acaricides leads to apparent cross-resistance as a consequence of crossing over; the two resistance genes are so close to each other that it would be difficult to segregate them once they came together on the same chromosome. -
CropUseCropUses:
apples, cherries, citrus, cotton, cucumbers, aubergines, fruits, greenhouse plants, ground covers, lathhouses, Japanese medlar, nuts, non-bearing tree fruit, melons, ornamentals, ornamental plants, ornamental trees, peas, pome fruits, shade plants, shrubs, strawberries, tea, tomatoes, watermelons, vegetables, vines
Vines
27.5 g ai/ha
Cotton
32-50 g ai/ha
Top fruit
5 g ai/ha
Pome fruit
101-150 g ai/ha
Citrus
5 g ai/ha
Strawberry
101-150 g ai/ha
Vegetables
5 g ai/ha
Tree nuts
101-150 g ai/ha
Tea
10 g ai/ha
Vines
101-150 g ai/ha
-
PremixSpirotetramat+Etoxazole
Fenpropathrin+Etoxazole
Etoxazole+Spirodiclofen
Diafenthiuron+Etoxazole
Bifenazate+Etoxazole
Abamectin+Etoxazole
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:359.4; Physical form:White, crystalline powder. Density:1.24 (20 °C); Composition:Tech. is 93-98%. Melting point:101-102 °C; Vapour pressure:2.18 ×10-3 mPa (25 °C); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 5.59 (25 °C); Solubility:In water 75.4 μg/l (20 °C). In acetone 300, methanol 90, ethanol 90, cyclohexanone 500, tetrahydrofuran 750, acetonitrile 80, ethyl acetate 250, xylene 250, n-hexane 13, n-heptane 13 (all in g/l, 20 °C).; Stability:No decomposition after 30 d (50 °C). Stable in alkali.
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats and mice >5000 mg/ kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >2000 mg/ kg; no skin or eye irritation (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation: LC50 for male and female rats >1.09 mg/l. ADI:( JMPR) 0.03 mg/ kg b.w. [1993].
-
Environmental Profile
Ecotoxicology:
Algae: NOEL for Selenastrum capricornutum >1.0 mg/l.Bees: LD50 (oral and contact) >200 μg/bee.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg. Sub-acute oral LD50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail >5200 ppm diet.Daphnia: LC50 (48 h) >40 ppm.Fish: LC50 (96 h) for Japanese carp 0.89 mg/l; (48 h) for Japanese carp >20, rainbow trout >40 ppm.Worms: NOEL (14 d) for Eisenia foetida >1000 ppm.Other aquatic spp.:Disruption of moulting was observed in aquatic arthropods.
Environmental fate:
Fate in soil:
Under laboratory aerobic conditions, etoxazole has a half-life of 19 days in Japanese soil, and 19-24 days in US sandy loam soil. The mean half-life generated from studies in seven soils is 20.5 days.
The half-life of etoxazole in soil photolysis studies is 22 - 24.3 days.
The Koc value is over 5,000 and etoxazole was immobile in 7 out of the 8 soils tested.
In field dissipation studies, the half life is 1-11 days.Fate in aquatic systems:
Etoxazole undergoes chemical degradation under acidic conditions (hydrolysis half-life around 10 days at pH 5.0) but is stable under basic conditions (half life 160-170 days at pH 7-9). -
Transport InformationHazard Class:O (Obsolete as pesticide, not classified)
Porduct NewsMore
EU proposes non-renewal of acaricide etoxazole
More US registration reviews planned
Cyhalofop-butyl Diclofop-methyl Fluroxypyr Imazapic Noviflumuron Tebufenpyrad Etoxazole Polyoxin d zinc salt
Related CompaniesMore
Country: China
Emamectin benzoate Imidacloprid Azoxystrobin Glyphosate Chlorothalonil Dinotefuran Carbofuran Glufosinate-ammonium Methomyl
Country: China
Clethodim Hexazinone Mesotrione Abamectin Acetamiprid Dimethoate Fipronil Imidacloprid Fosetyl-aluminium 2,4-D
Country: China
Boscalid Prosulfocarb Trifloxystrobin Thiobencarb Prothioconazole Etoxazole Cyhalofop-butyl Chlorothalonil Azoxystrobin 2,4-D
POSITIVE GROUP INVESTMENTS LIMITED
Country: Serbia

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe