-
Common NameFenarimol
-
中文通用名氯苯嘧啶醇
-
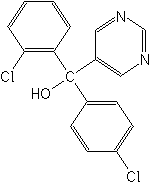
IUPAC(RS)-2,4′-dichloro-α-(pyrimidin-5-yl)benzhydryl alcohol
-
CASα-(2-chlorophenyl)-α-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-pyrimidinemethanol
-
CAS No.60168-88-9
-
Molecular FormulaC17H12Cl2N2O
-
Molecular Structure
-
Category
-
ActivityFenarimol inhibits fungal growth by adversely affecting the formation of the fungal sterol ergosterol
-
CropUsefor use on fruit and nut crops such as apples, cherries, filberts (nonbearing), grapes, hops, pears, and pecans, as well as on ornamental plants, trees, and grasses and turf lawns.
-
Disease Spectrumfor control of such pests as scab, powdery mildew, rusts, and leaf spot.
-
Weed Spectrum
-
Pest Spectrum
-
Premix
-
Physical PropertiesMolecular weight:331.2; Physical form:Off-white crystals. Density:1.40; Composition:Tech. is 98%. Melting point:117-119 °C; Vapour pressure:0.065 mPa (25 °C) by vapour pressure balance; Henry constant:1.57 × 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 ( calc.); Partition coefficient(n-octanol and water):logP = 3.69 ( pH 7, 25 °C); Solubility:In water 13.7 mg/l ( pH 7, 25 °C). In acetone 151, methanol 98.0, xylene 33.3 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Readily soluble in most organic solvents, but only slightly soluble in hexane.; Stability:Decomposed rapidly by sunlight, aqueous DT50 c. 12 h. Hydrolytically stable up to 52 °C ( pH 3-9).;
-
ToxicologyOral:Acute oral LD50 for rats 2500, mice 4500, dogs >200 mg/ kg. Percutaneous:Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Mild eye irritant; non-irritating to skin (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation:No adverse effect seen when rats exposed for 1 h to 2.04 mg tech./l air. Phytotoxicity:Non-phytotoxic when used as directed. If used in excessive amounts, abnormal leaf development and darker green colouration may result. ADI:( JMPR) 0.0008 mg/
-
Environmental ProfileEcotoxicology:
Algae:For Scenedesmus subspicatus ErC50 5.1 mg/l, NOEC 0.59 mg/l; for Raphidocellis subcapitata ErC50 1.5 Bees: LD50 (48 h) (oral) >10 mg/bee; (contact) >100 mg/bee.Birds:Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2000 mg/ kg.Daphnia: EC50 (48 h) 5.1 mg/l, NOEC 4.0 mg/l.Fish: LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 4.1, bluegill sunfish 5.7 mg spp.:Harmless to Typhlodromus pyri, Aphidius rhopalosiphi, Poecilus cupreus and Chrysoperla carnea.
Environmental fate:
Animals:In mammals, following oral administration, fenarimol is rapidly excreted.Soil:DT50 >365 d under aerobic conditions in laboratory soil (28% sand, 14.7% clay, 57.3% silt, 2.3% o.m., pH 6.1). Field DT50 14-130 (average 79) d. Koc -
Transport InformationSignal Word:CAUTION; Hazard Class:III(Slightly hazardous)
Porduct NewsMore
Carbendazim fungicide wins victory in Brazilian Parliament
Corteva presents new pre-emergent herbicide Linear for sugarcane in Brazil
Picloram Triclopyr Aminopyralid
Revolutionizing disease prevention: BASF launches new rice fungicide Cevya® in China
Thiamethoxam is allowed again in Brazil by a judicial decision
Bayer develops alternative to glyphosate herbicide
Colombia’s Constitutional Court bans chlorpyrifos
ADAMA Canada moves forward with lambda-cyhalothrin sales for 2023
Mexico: Import of glyphosate drops from 16,500 tons to 8,200 tons

 0
0 Subscribe
Subscribe